hypothesis
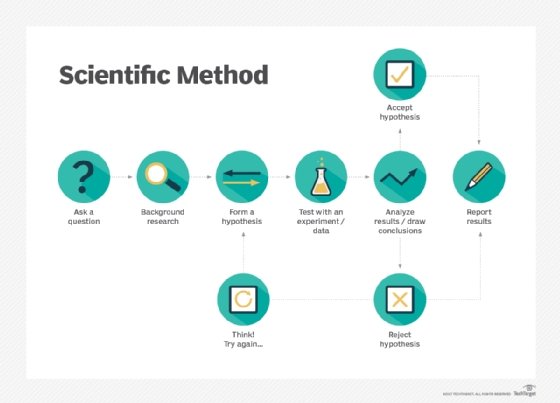
A hypothesis (plural: hypotheses), in a scientific context, is a testable statement about the relationship between two or more variables or a proposed explanation for some observed phenomenon. In a scientific experiment or study, the hypothesis is a brief summation of the researcher's prediction of the study's findings, which may be supported or not by the outcome. Hypothesis testing is the core of the scientific method.
The researcher's prediction is usually referred to as the alternative hypothesis, and any other outcome as the null hypothesis -- basically, the opposite outcome to what is predicted. (However, the terms are reversed if the researchers are predicting no difference or change, hypothesizing, for example, that the incidence of one variable will not increase or decrease in tandem with the other.) The null hypothesis satisfies the requirement for falsifiability: the capacity for a proposition to be proven false, which some schools of thought consider essential to the scientific method. According to others, however, testability is adequate, on the grounds that if there is sufficient support for a hypothesis it is not necessary to be able to conceive of a contrary outcome.
A simple hypothesis might predict a causal relationship between two variables, meaning that one has an effect on the other. Here's an example: More hours spent studying for an exam result in higher grades. Hours spent studying, in this statement, is the independent variable and grades is the dependent variable. The independent variable is manipulated and the dependent variable is measured to see how it is affected as the independent variable changes.
A complex hypothesis is similar to a simple one but includes two or more independent variables or two or more dependent variables. In the first case, for example, the hypothesis might be that more hours studying and more classes attended lead to higher grades; in the second case, the hypothesis might be that more hours studying lead to higher grades and a shorter amount of time required to write the exam.
Hypotheses don't necessarily predict causality. In statistics, for example, a hypothesis might predict simple correlation -- for example, that increased incidence of the independent variable is associated with a decrease in the dependent variable, although there is no supposition that one causes the other.