chief privacy officer (CPO)
What is a chief privacy officer (CPO)?
A chief privacy officer (CPO) is a corporate executive charged with developing and implementing policies designed to protect employee and customer data from unauthorized access.
A privacy policy explains how an organization handles any customer, client or employee information gathered in its operations. A corporate privacy policy should also explain practices and procedures designed to ensure that privacy requirements are met.
Other elements of the CPO job include maintaining a comprehensive and current knowledge of both corporate operations and privacy laws, as well as communicating details of the company's privacy policy to staff and customers alike. The CPO is typically the organization's point person for media and other external inquiries about privacy-related matters.
To effectively meet the challenges of the job, the CPO must work in cooperation with other C-level executives, particularly those whose areas of concern overlap, such as the CIO, CSO, the chief data officer (CDO) and the chief compliance officer (CCO).
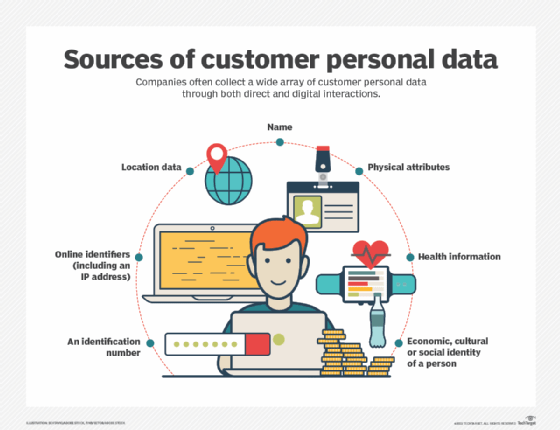
Evolving scope of the CPO's responsibilities
In the wake of global privacy regulations like the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA), CPOs now navigate a complex landscape of compliance requirements.
The CPO is integral in shaping the strategic direction of their organization to ensure privacy considerations are embedded in business processes and align with international standards. The CPO must maintain the trust of customers and stakeholders while simultaneously preventing legal and financial repercussions associated with noncompliance.
CPOs hold a strategic position within the corporate hierarchy, influencing business practices and technology decisions to safeguard privacy. Their collaboration extends beyond the IT department, encompassing legal, compliance and business units to integrate privacy into the organizational fabric.
The strategic nature of the role necessitates a holistic understanding of the business and its objectives, ensuring privacy considerations are balanced with innovation and growth.

Career path and qualifications for CPOs
Aspiring CPOs typically come from legal, compliance or information technology backgrounds, with a strong understanding of privacy laws and data protection principles.
Key qualifications include a combination of formal education, such as law or information security degrees, and professional certifications in privacy and data protection. Successful CPOs possess excellent analytical, communication and strategic thinking skills, enabling them to navigate the complexities of privacy in the digital age.
Additionally, CPOs need the experience required to lead privacy awareness and training initiatives within their organizations to foster a culture of privacy and ensure compliance across all levels. By educating employees about privacy principles and data protection practices, CPOs empower their workforce to act as privacy advocates, reinforcing the organization's commitment to safeguarding personal information.
The impact of technological advancements on the role of CPO
With the rapid advancement of technologies like AI and big data, CPOs must oversee data protection impact assessments and advocate for privacy by design in new products or services.
Their understanding of these technological advancements is crucial in identifying and mitigating privacy risks before they materialize, ensuring that new technologies are implemented responsibly and in line with privacy considerations.
This requires that the CPO works closely with the cybersecurity team to address data breaches and incident responses. This collaboration ensures that privacy considerations are integral to security strategies, particularly in managing and mitigating the impact of data breaches on customer trust and compliance.
It also underscores the need for the CPO to stay ahead of emerging trends, such as the implications of new technologies on data privacy and evolving regulatory landscapes. This C-level executive plays a critical role in adapting organizational strategies to meet these changes, ensuring that privacy considerations keep apace with technological advancements and market dynamics.
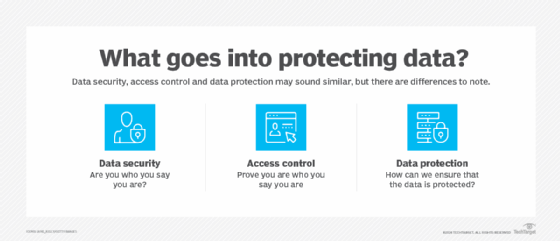
By addressing these expanded responsibilities and challenges, the CPO's role is seen as increasingly vital in guiding organizations through the complexities of privacy in the digital world, ensuring not only compliance but also fostering trust and ethical data practices.
The importance of a data privacy audit can't be underestimated due to the proliferation of customer data, more stringent regulations and sophisticated cyberthreats. Check out this step-by-step guide on how to conduct a data privacy audit.
