Perl
What is Perl?
Perl is a family of script programming languages that is similar in syntax to the C language. It is an older, open source, general use, interpreted language.
Perl was developed with usability in mind. Its efficient design lets developers do a lot with a little bit of code. Its nickname is the "Swiss Army chainsaw" of the internet.
Perl is simpler to learn and code with than more structured languages, such as C and C++. Nevertheless, the language is used to develop advanced programs. The language is often used to develop common gateway interface (CGI) programs because it has good text manipulation capabilities and the ability to deal with binary files.
Design and features of Perl
Perl includes popular Unix facilities, such as sed, awk and tr. As an interpreted language, code can run as is, and instructions are executed without first compiling the entire program into machine language instructions.
However, Perl can be compiled before execution into C code or cross-platform bytecode. When compiled, a Perl program is almost as fast as a fully pre-compiled C language program. A plugin is available for some servers, such as Apache, loading Perl permanently in memory. This reduces compile time and results in faster execution time of CGI Perl script.
Here are additional Perl features:
- Glue language. As a glue code language, Perl makes it easier for programmers to integrate otherwise incompatible interfaces and components. It features a database integration interface that supports third-party databases, like MySQL, Oracle, Postgres and Sybase.
- Embedding. Perl can be embedded in database servers and web servers.
- Text processing. It includes powerful text processing tools that enable it to work with markup languages, like Hypertext Markup Language and Extensible Markup Language.
Perl syntax and code examples
Like all programming languages, Perl follows a basic syntax for writing code. It contains keywords and variables for storing expressions and statements that execute the program's logic.
A Perl program always begins with this line of code:
#!/usr/bin/perl
This is the shebang line. It lets the computer know that the following text will be Perl code and calls the Perl interpreter. Perl programs must pass through the interpreter to execute.
After that, a user could write a basic "Hi there, world!" script:
print "Hi there, world!\n"
The output would be the following:
"Hi there, world!"
Users could also declare a variable. In Perl, the variable is predefined by a variable indicator -- a $, @ or %. These define the data type:
- Scalar data types, which store numbers, strings and references, are preceded by $.
- Arrays, which store ordered lists of scalars, are preceded by @.
- Hashes, which store sets of Key-value pairs, are preceded by %.
To declare a simple string, which is a scalar data type, $ should be used:
$str = "My name is Sam";
print "$str\n"
Here, the output would be the following:
"My name is Sam"
Perl also has many special variables, which are denoted by altering the normal variable indicators, as shown in this list.
An example of a more advanced program from Perl.org is below. This program sends an email using Perl script:
#!/usr/bin/perl
use strict;
use warnings;
# create the email message
use Email::MIME;
my $note = Email::MIME->create(
header_str => [
From => '[email protected]',
To => '[email protected]',
Subject => 'Happy New Year!',
],
attributes => {
encoding => 'quoted-printable',
charset => 'ISO-8859-1',
},
body_str => "Wishing you a very happy New Year!\n",
);
# send the email
use Email::Sender::Simple qw(sendmail);
sendmail($note);
Pros and cons of using Perl
Perl has several advantages, as well as some disadvantages.
Advantages
Perl's advantages include the following:
- Options. Users have a lot of alternatives in how they write a program or solve a problem using Perl.
- Flexible. The language's design and syntax let users code using their own programming style.
- Open source. Perl is free for anyone to access, develop and use on a variety of platforms.
- Availability. It is pre-installed in many places, and more than 25,000 Perl modules are available on the Comprehensive Perl Archive Network. It is also implemented on most operating systems.
Disadvantages
Perl's major disadvantage is that it's a relatively messy language in a number of ways:
- Hard to read. Some developers claim Perl is difficult to read and less streamlined than newer languages, like Python. Because there many ways to write a Perl program, it can lead to disorganized, untidy code.
- Difficult to debug. Because Perl code can be obscure or messy, debugging and fixing problems can be difficult.
- Performance flaws. The same flexibility that benefits Perl users can also cause it to be slow. That's because this flexibility can lead to inefficiencies and redundancy taking it longer to compile.
Perl vs. Python
Perl and Python have a shared history. Both were invented to simplify scripting. Perl was developed to give a C-like structure to Unix scripts. Python was invented to make C simpler and ready to script with.
Perl and Python are similar syntactically, and translating from Perl to Python is relatively easy with a few major syntax changes.
However, here are four key differences:
- Lines written in Perl end in a semicolon.
- Perl contains curly braces and indentation; Python does not.
- Variable names in Perl are styled using a variable indicator, like $x, %x and x. Variable names in Python are styled without a variable indicator, like x.
- The print statement in Python adds a new line at the end of output.
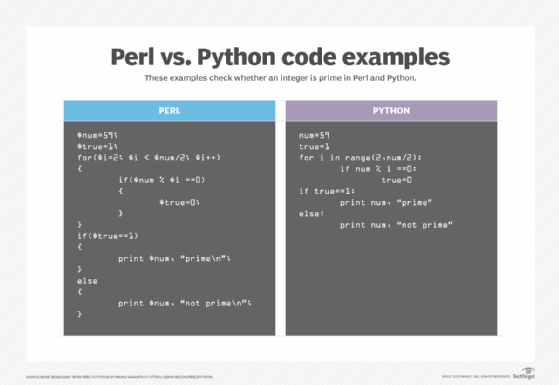
Other differences include the following:
- Perl can be messy, and Python is more streamlined.
- There are many ways to do things in Perl, whereas Python is designed to provide one clear path to any given function.
- Python is easier to read than Perl.
- Python is considered one of the best coding languages to learn and one of the easiest for novice developers.
- Python is a newer language than Perl.
- Perl is integrated with web application source code.
- Python has a reputation as a dynamic programming language with a broad array of applications -- from web development to machine learning -- making it a popular language.
- The open source developer community is more supportive of Python.
History and future of Perl
Programmer Larry Wall created the first version of Perl in 1987. Perl was originally said to stand for "Practical Extraction and Reporting Language," but that name is no longer used. Wall prefers to use "Perl" for the language itself and "perl" for any interpreter or compiler of the language.
Perl 5 first became available in 1994. The latest stable version of Perl is 5.34.0, according to Perl.org.
Perl 6 is rooted in the same ancestor language as Perl 5 but is a separate programming language. It has its own design team of open source volunteers.
The Perl 6 project began after the 2000 Perl Conference, but the first official version of the language, version 6.c, wasn't available until December 2015. Perl 6 was renamed Raku in 2019.
Today, Perl refers to Perl 5. Work on Perl 7 began in 2020. It is expected to be available in 2021.
Learn more about Perl and four other programming languages that are still influential but are likely to be obsolete in the next decade.
