Bohr radius
What is Bohr radius?
The Bohr radius is a physical constant that represents the most probable distance between the electron and nucleus of a hydrogen atom at its ground state (lowest energy level). The constant's value, symbolized a0, is approximately 5.29177210903(80) x 10-11 meters (m). The parenthetical number (80) indicates the level of standard uncertainty, which is 0.00000000080 x 10-11. The relative standard uncertainty is 1.5 x 10-10.
| Unit system | Approximate value |
| SI units |
5.29 x 10-11 m (meters) |
| Imperial units |
2.08 × 10-9 in (inches) |
| Natural units |
2.68 × 10-4 /eV (electron volts) |
The Bohr radius constant for a hydrogen atom can be stated in different units, including the International System of Units (SI), imperial units and natural units.
In addition, the constant can be converted from meters to centimeters (5.29177 x 10-9 cm), to nanometers (0.0529177 nm) or to angstroms (0.529 Å). The constant is also equivalent to about 1/10,000 of the wavelength of a ray of blue visible light.
How to derive the Bohr radius?
The value of the Bohr radius has been adjusted slightly since it was introduced in 1913 by Niels Bohr (1885-1962), a Danish physicist and philosopher. The latest official value for the Bohr radius was published in 2018 by the Committee on Data of the International Science Council (CODATA), which works to promote international collaboration to advance open science and improve the availability and usability of data.
The CODATA value for the Bohr radius is based on the formula a0 = ℏ/αmec, where:
- a0 is the Bohr radius.
- ℏ is the reduced Planck constant.
- α is the fine-structure constant.
- me is the mass of an electron.
- c is the speed of light in a vacuum.
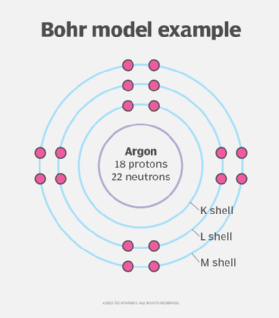
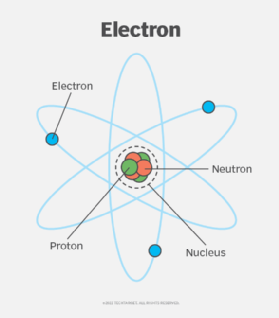
The Bohr radius is derived from the Bohr model of the atom, which Niels Bohr proposed in 1913 to describe the behavior of an atom's electrons. Bohr envisioned atoms as consisting of small, dense nuclei with positive electric charge, around which negatively charged electrons orbit in circular paths, similar to how planets orbit the sun. The Bohr model explained how an electron is "quantized" to its orbit so it doesn't fall into the nucleus.
Nowadays, physicists consider the Bohr model to be an oversimplification of the atomic structure; the electrons are thought to surround the nucleus in spherical probability zones called shells. However, the Bohr radius is still a useful constant because, in a sense, it represents the smallest mean radius normally attainable by a neutral atom.
Learn about the role atomic physics plays in quantum computing and why you should pay attention to these developments.
