What Is Bandwidth? Definition, Meaning, and Details
Bandwidth, with various technical interpretations, now commonly refers to the capacity of a transmission medium, like an internet connection, to handle information per unit of time.
In practical terms, a higher bandwidth internet connection enables faster transfer of data, such as video files, compared to a lower bandwidth connection.
Typically, bandwidth is denoted in bits per second, such as 60 Mbps or 60 Mb/s, representing a data transfer rate of 60 million bits (megabits) per second.
The Significance of Grasping Bandwidth Understanding
It’s common to overlook bandwidth as a technical phrase that may not appear important unless you’re familiar with internet device settings. Understanding what bandwidth is and how it connects to your network, on the other hand, can help you optimize your setup for faster internet connections as needed.
If your internet connection is suffering unexpected slowdowns, you may be wondering about bandwidth. You might be thinking if you must upgrade your bandwidth or if you’re getting the promised performance for your money.
Alternatively, you may be thinking about purchasing a gaming console or video streaming service and want to be sure it won’t disrupt the rest of your network. For many users, these activities generally take the most bandwidth.
What is the amount of bandwidth you currently have available? (And what is the required amount?)
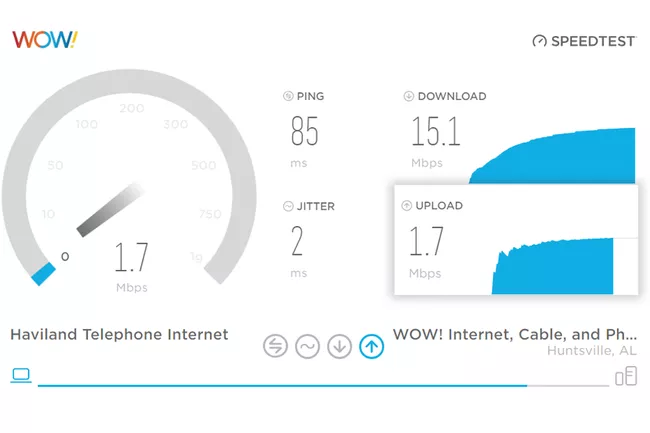
You can use the “How to Test Your Internet Speed” instruction to determine how much available bandwidth you have. Although there are different ways available, Internet speed test websites are often utilized for this purpose.
The required bandwidth largely depends on your intended internet usage. Generally, having more bandwidth is preferable, within the constraints of your budget.
For casual activities like browsing Facebook and occasionally watching videos, a low-end high-speed plan should be sufficient.
If you have specific internet needs, you should seek official bandwidth recommendations from the provider you intend to utilize. For example, if your current internet connection is working properly but you want to subscribe to a movie streaming service, their website might specify the minimum suggested bandwidth for uninterrupted watching.
If you have multiple TVs streaming Netflix, along with numerous computers, tablets, and other devices engaged in various activities, it’s recommended to opt for as much bandwidth as your budget allows. You won’t regret having a higher bandwidth capacity.
- Learn why your laptop-computer is slower down and how to fix it
- Learn how to increase your internet speed
- Do you know the meaning of Kbps and how it affects your computer speed
Drawing a Parallel: Bandwidth as an Analogy to Plumbing
Comparing bandwidth to plumbing can be quite enlightening!
In this analogy, data can be likened to the water flowing through pipes, while available bandwidth corresponds to the size of the pipes themselves.
Simply said, as bandwidth increases, so does the capacity for data to flow through in a particular time frame, much as larger pipes allow more water to move through in the same amount of time.
Assume you’re watching a movie while someone else is playing an online multiplayer game and a few others on your network are downloading files or watching videos on their phones. You may notice sluggishness or interruptions due to a lack of bandwidth.
Returning to the plumbing analogy, turning on several taps and showers (data downloads to devices) will result in decreasing water pressure at each point (perceived “speed” on each device) if the water line to your home (representing the bandwidth) remains the same size. This happens because the residence has a restricted amount of water (bandwidth) on the network.
Essentially, bandwidth is a fixed amount determined by your subscription. While one person may be able to stream high-definition videos smoothly, adding more download requests to the network means each device will receive only a portion of the total capacity.
For example, if a speed test shows that my download speed is 7.85 Mbps, it means that I could download a 7.85 megabit (or 0.98 megabyte) file in one second, without interruptions or other bandwidth-intensive programs. With this bandwidth, I could download approximately 60 MB of data each minute or 3,528 MB per hour, which is roughly equivalent to a 3.5 GB file, which is comparable to a full-length DVD-quality movie.
However, if someone else on my network simultaneously tries to download a similar file, the download time will double. This is because the network can only accommodate a certain amount of data being downloaded at any given time, and it must allocate some of the available bandwidth to the second download as well.
Technically, the network would now have to handle 3.5 GB + 3.5 GB, for a total of 7 GB of data to be downloaded. Because bandwidth capacity is a set quantity provided by your internet service provider (ISP), the same logic applies: with a 7.85 Mbps network, downloading the 7 GB file would now take two hours, just as downloading half that amount would take one hour.
Differentiating between Mbps and MBps
It is critical to recognize that bandwidth can be measured in a variety of units (bytes, kilobytes, megabytes, gigabits, and so on). One unit may be used by your Internet service provider, another by a testing service, and yet another by a video streaming service. To avoid overpaying for internet service or ending up with insufficient capacity for your needs, it’s critical to understand the link between these phrases and how to convert between them.
For example, 15 MB does not equal 15 Mbs (notice the lowercase “b”). The former represents 15 megabytes, while the latter stands for 15 megabits. Because a byte has 8 bits, these two values differ by a factor of 8.
These two bandwidth values would be 15 and 1.875 in megabytes (MB), respectively (since 15 divided by 8 = 1.875). When measured in megabits (Mb), however, the first result becomes 120 Mbps (since 15 multiplied by 8 is 120), whereas the second value stays 15 Mbps.
Managing Bandwidth Usage
Certain software allows you to control and restrict the amount of bandwidth used by a program, which can be quite useful if you want the program to run without consuming too much internet. This purposeful bandwidth limitation is frequently referred to as bandwidth control.
Several download managers, including Free Download Manager, as well as various online backup services, cloud storage services, torrenting programs, and routers, have bandwidth management options. Because these applications and apps consume large quantities of bandwidth, the ability to limit their consumption is a reasonable and practical option.
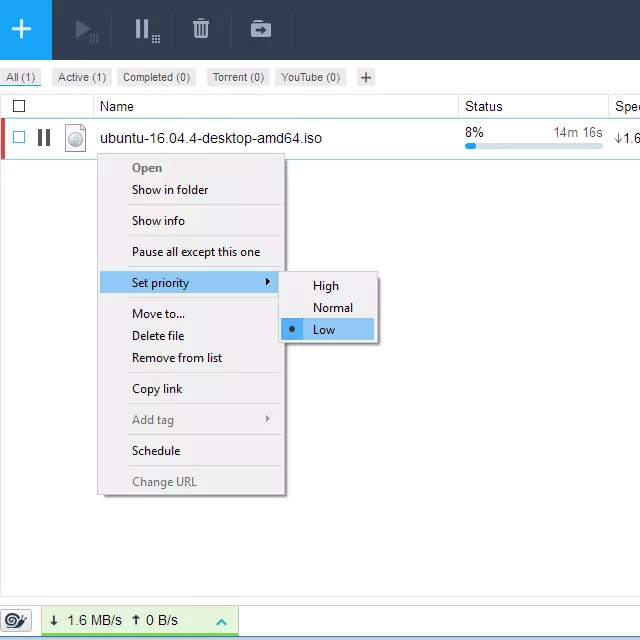
As an example, suppose you want to download a 10 GB file. Instead of letting it to take all available bandwidth for hours, use a download manager that allows you to limit the download to only 10% of the available bandwidth.
While this approach would certainly increase the overall download time, it would significantly free up more bandwidth for other time-sensitive activities, such as live video streaming.
Bandwidth throttling is a concept comparable to bandwidth control. It entails internet service providers purposefully blocking or regulating specific types of traffic. This could be done to limit activities such as Netflix streaming or file sharing, or to relieve network congestion by imposing bandwidth limits at specified times of day.
More than just the quantity of available bandwidth influences network performance. Latency, jitter, and packet loss are also important factors in assessing network performance quality. Furthermore, old hardware, viruses, browser add-ons, and a sluggish Wi-Fi connection can all contribute to slow internet performance.
Frequently Asked Question
Is it possible for me to monitor and view the usage details of the current bandwidth consumption?
There are several methods for monitoring network traffic. You can, for example, use your router’s built-in functions or third-party applications made expressly for this purpose. Additionally, the website of your Internet Service Provider may give bandwidth monitoring tools and information.
How much bandwidth does Netflix consume per hour of streaming?
Netflix has four data usage options, each with its own data consumption rate. Low consumes up to 0.3 GB per hour, Medium consumes up to 0.7 GB per hour, High consumes 1-7 GB per hour (depending on the video quality selected), and Auto dynamically adjusts the streaming quality based on the internet connection speed. Access your Netflix account page via a web browser, navigate to your account page > Profile & Parental Controls > Profile > Playback Settings > Change.
When can I expect my bandwidth to be reset?
Bandwidth is reset on a monthly basis according to the specified date in the Site Settings Tab of your Site Manager’s page.
I am experiencing issues with my monthly bandwidth reset. What steps should I take to resolve this?
To ensure you’re viewing the most up-to-date content on your site, it’s recommended to regularly clear your cache and cookies. Additionally, please allow a 12-hour grace period for your meter to reset, as unscheduled maintenance may occasionally occur, which could impact the automatic reset process.
ad


Comments are closed.